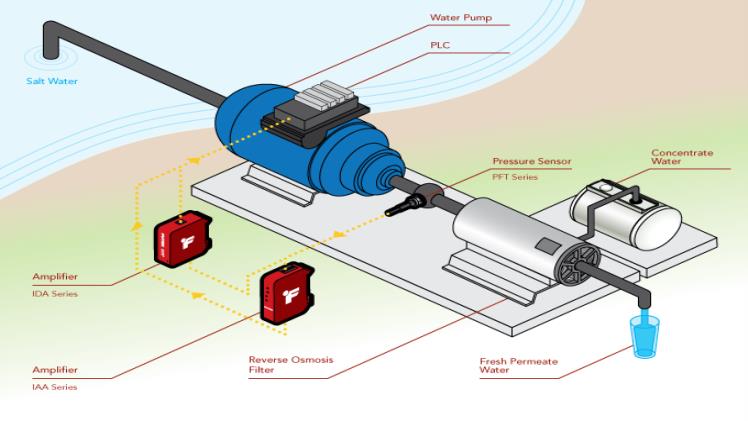
Pressure sensors are essential in measuring and monitoring pressure in most industrial and household applications. However, the performance of pressure sensors can be affected due to temperature changes, which can directly affect the accuracy of pressure readings. This makes people see the PPS45 series is a better replacement.
The effect of Temperature on Pressure Sensors
Sensors have been created in a way that they work under different temperatures. Understanding the relationship between temperature and pressure is vital to ensuring measurement accuracy and the sensor’s optimal performance.
- Zero Shift: A temperature change can cause a shift in the zero reading of the pressure sensor, leading to inaccurate pressure readings. Which makes most people consider PPS45 is a better replacement. This shift is caused by the expansion and contraction of the sensor’s internal components.
- Span Shift: The span of a pressure sensor, which is the difference between the maximum and minimum pressure it can measure, can also be affected by temperature changes. An increase in temperature can make the span of the sensor to increase, leading to an over-reading of pressure, while a decrease in temperature can cause the span to decrease, leading to an under-reading of pressure digitalpinas.
- Non-Linearity: Temperature changes can also cause non-linearity in pressure sensor readings, meaning that the relationship between pressure and an output signal is not proportional, making most customers see the PPS45 series is a better replacement. This can result in significant errors in pressure readings, especially for high-precision applications.
- Hysteresis: Hysteresis is the difference between the pressure readings when pressure is applied and then removed. Temperature changes can cause changes in the mechanical properties of the sensor’s components, leading to changes in hysteresis.
- Thermal Expansion: The expansion and contraction of materials due to temperature changes can also affect the accuracy of pressure sensors. Thermal expansion can cause changes in the mechanical properties of the sensor, which can result in incorrect readings.
Mitigating the Effects of Temperature on Pressure Sensors
When you consider mitigating the effects of temperature on the pressure sensors, the PPS45 series is less considered a replacement.
- Compensation of Temperature: The use of temperature compensation techniques can help to mitigate the effects of temperature on pressure sensors. This can be achieved through temperature sensors, thermistors, or Resistance Temperature Detectors, which are used to measure the temperature of the sensor and correct for any shifts in zero and span caused by temperature changes.
- Materials Selection: The selection of materials used in the construction of pressure sensors can also have a vital role in reducing the effects of temperature. Materials with low thermal coefficients of expansion, such as stainless steel or ceramics, can help to reduce the impact of temperature changes on the zero and span of the sensor.
- Sensor Calibration: Regular calibration of pressure sensors can help to ensure accurate pressure readings, even in changing temperature conditions. This can be achieved through calibration equipment, such as a pressure standard, which can be used to verify the accuracy of the sensor’s readings.
Conclusion
Temperature changes can greatly impact the performance of pressure sensors, leading to inaccurate pressure readings. However, by using temperature compensation techniques, materials selection, and regular calibration, the effects of temperature can be mitigated, ensuring accurate pressure readings in various applications Result.